Sleep and Beauty®
30 Capsules
Helps promote relaxation and sleep
Supports skin, nail and hair structure
Attributes
- Sleep aid
- Helps promote relaxation and sleep
- Helps support skin, nail and hair structure
Suggested Use
Oral. Recommended for adults.
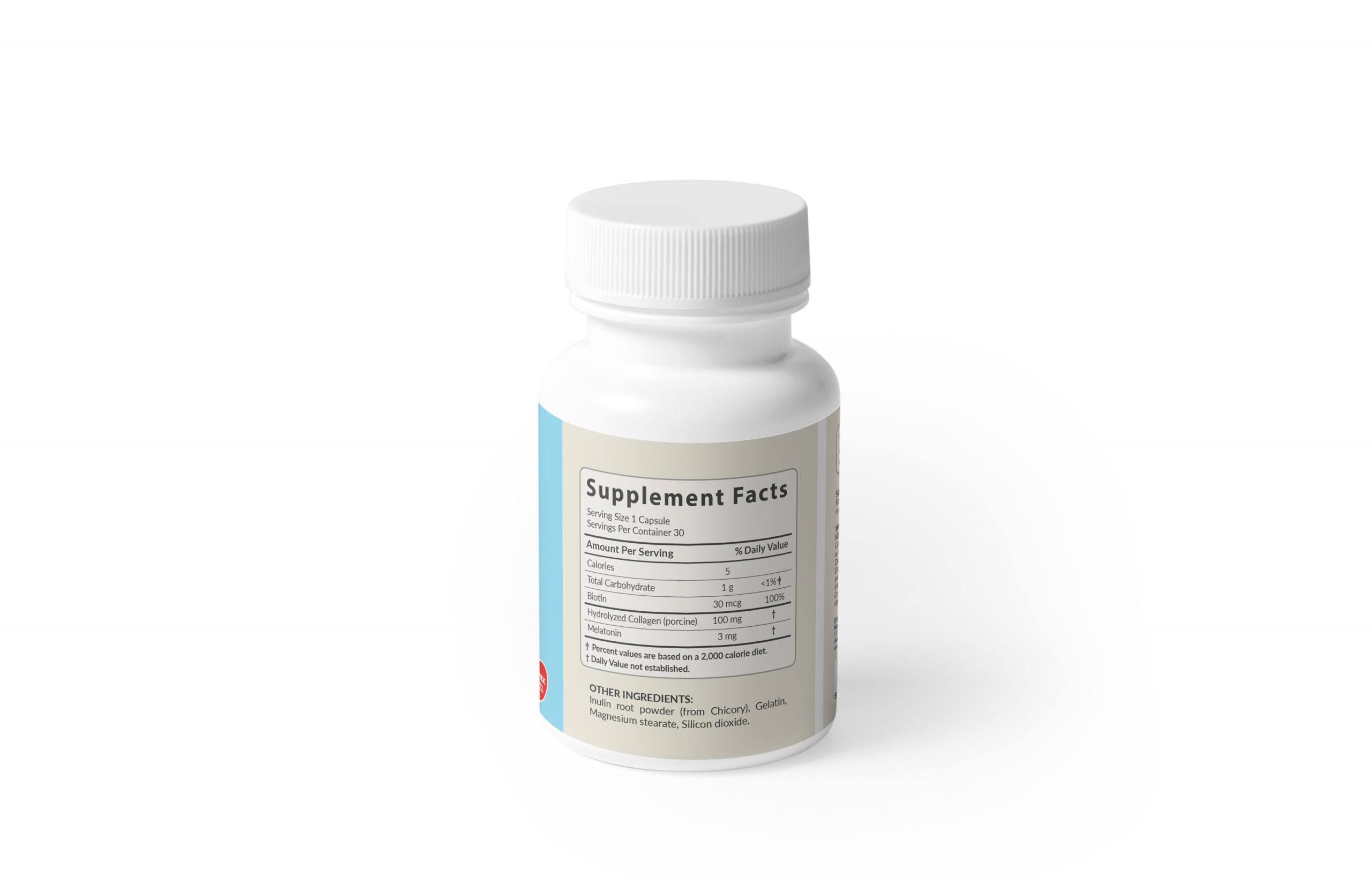
Active Ingredients
Hydrolyzed Collagen, Biotin and Melatonin
Recommended Use
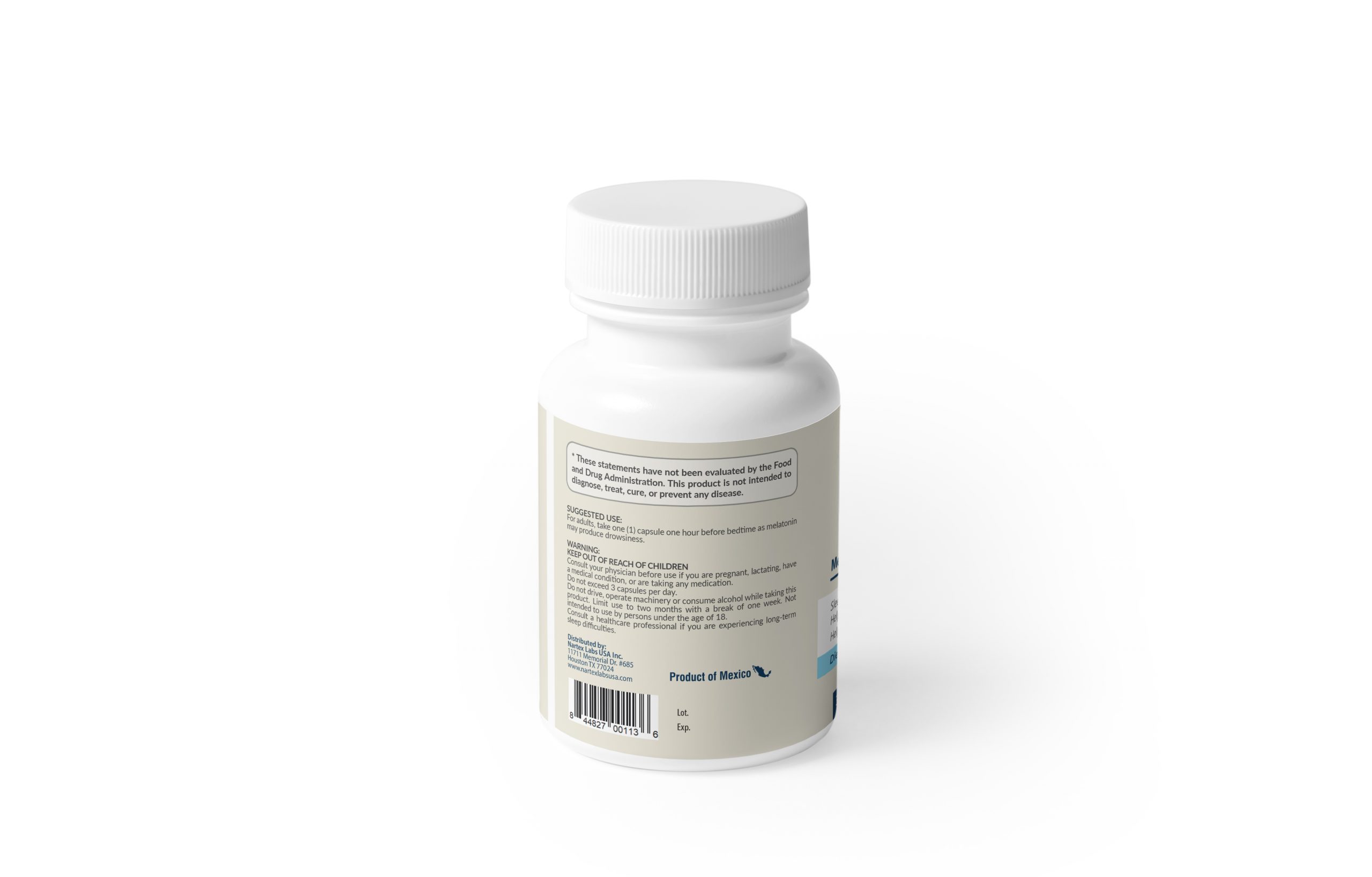
For adults, take one 1 capsule one hour before bedtime as melatonin may produce drowsiness.
Keep out of reach of children. Consult your physician before use if you are pregnant, lactating, have a medical condition, or are taking any medication. Do not exceed 3 capsules per day. Do not drive, operate machinery, or consume alcohol while taking this product. Limit use to two months with a break of one week. Not intended to use by persons under the age of 18. Consult a healthcare professional if you are experiencing long term sleep difficulties.
Tell Me More!
Our body naturally produces Melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep/wake cycle (circadian rhythm). This is why findings are encouraging to use melatonin as a solution for those with sleep disturbances.4,5
Collagen is a protein already found within the body (nails, hair and skin). However, supplementation may be needed in order to hydrate the skin and reduce the appearance of wrinkles1.
Biotin is a water–soluble vitamin and coenzyme that promotes hair, skin, and nails growth2. Additionally, it is important for adequate fat production in the body and essential to avoid dermatitis, alopecia and some other skin infections3.
- Czajka, A., Kania, E., Genovese, L., Corbo, A., Merone, G., Luci, C., Sibilla, S. 2019. Daily oral supplementation with collagen peptides combined with vitamins and other bioactive compounds improves skin elasticity and has beneficial effect on joint and general wellbeing. Nutrition Research.
- Zempleni, J., Wijeratne, S. S., & Hassan, Y. I. (2009). Biotin. Biofactors, 35(1), 36-46.
- Mock, D. M. (1991). Skin manifestations of biotin deficiency. In Seminars in Dermatology. Vol. 10, No. 4, p. 296-302.
- Hardeland, R., Pandi-Perumal, S. R., & Cardinali, D. P. (2006). Melatonin. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 38(3), 313-316
- Blask, D. E. (2009). Melatonin, sleep disturbance and cancer risk. Sleep medicine reviews, 13(4), 257-264.